Emerging Trends in Data Wiping for ITAD
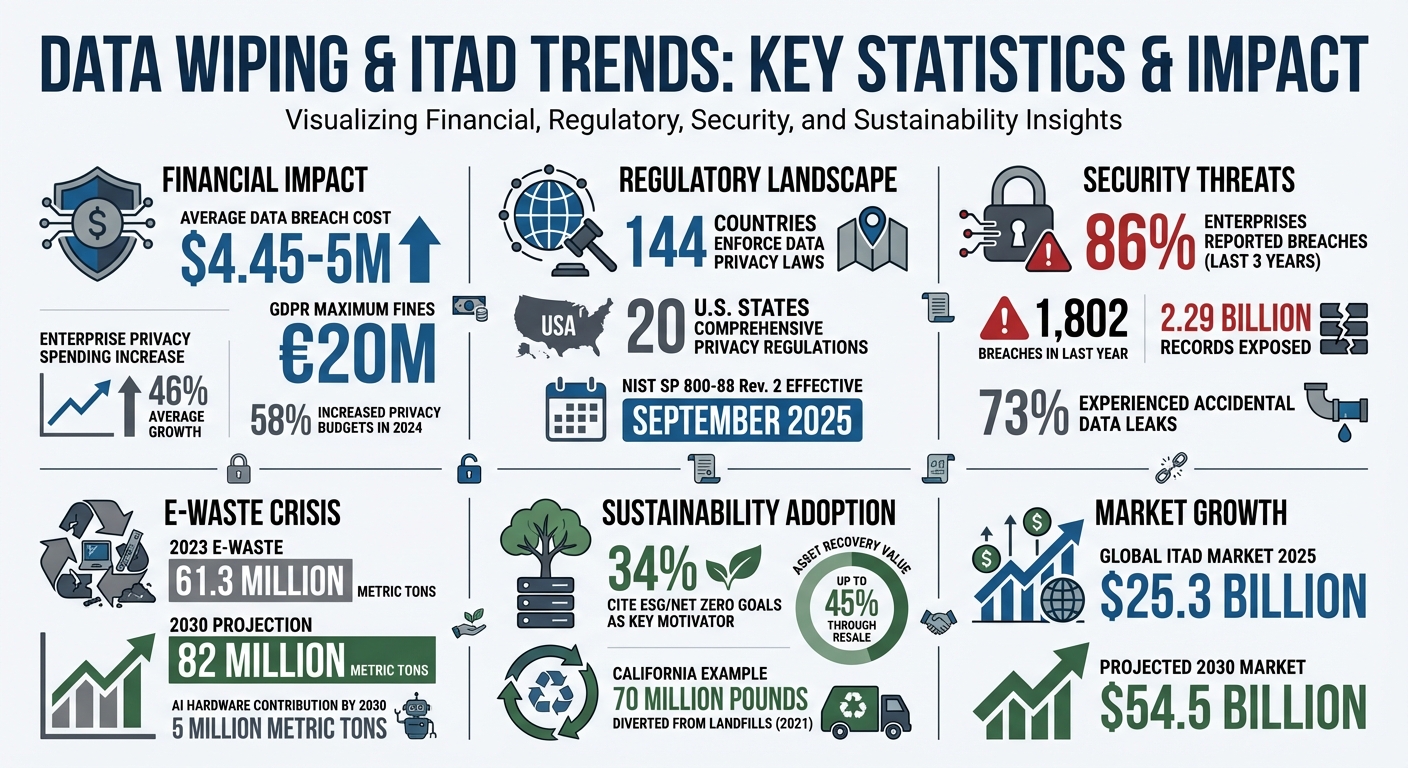
Certified data wiping is now a cornerstone of IT asset disposition (ITAD). It ensures sensitive data is securely erased, compliance with strict regulations like NIST SP 800-88 and GDPR, and supports hardware reuse to reduce e-waste. With global e-waste projected to reach 82 million metric tons by 2030, businesses are shifting to software-based erasure methods that protect data and extend device life.
Key Takeaways:
- Why It Matters: Data breaches cost an average of $5M, and improper disposal risks compliance penalties (e.g., GDPR fines up to €20M).
- Trends Driving Demand: Stricter data laws (144 countries enforce privacy laws), rising cybersecurity threats, and hardware upgrades.
- Methods: Software erasure (e.g., Cryptographic Erase) preserves functionality, while physical destruction (shredding, degaussing) is reserved for sensitive cases.
- New Standards: NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 2 (2025) and IEEE 2883-2022 address modern storage challenges like SSDs and NVMe drives.
- Automation: AI and ERP integrations streamline workflows, enabling secure, large-scale data wiping and real-time reporting.
- Sustainability Goals: Certified data wiping supports reuse, helping businesses achieve landfill-free operations and ESG targets.
For businesses, choosing between on-site and off-site destruction depends on security needs and volume. Providers like Rica Recycling in California combine certified data wiping with zero-landfill policies, ensuring compliance and reducing environmental impact.
Data Wiping & ITAD Statistics: Compliance Costs, E-Waste Projections & Security Trends 2025
Why Certified Data Wiping Demand Is Increasing
What's Driving the Data Wiping Market
The demand for certified data wiping is on the rise, fueled by stricter regulations, growing cybersecurity threats, and the rapid pace of technological upgrades.
The regulatory environment has become increasingly intricate. Currently, 144 countries enforce data privacy laws, with 20 U.S. states having comprehensive privacy regulations. The financial implications are significant - 58% of enterprises increased their spending on data privacy compliance last year, with budgets growing by an average of 46%.
Cybersecurity challenges are another major factor. Over the past three years, 86% of enterprises reported breaches, with each breach costing an average of $4.45 million. In the last year alone, 1,802 breaches exposed 2.29 billion records. Additionally, 73% of enterprises experienced accidental data leaks during this period. Certified data wiping has become a vital safeguard, serving as the final barrier to prevent data leaks.
The push for technology upgrades also plays a substantial role. The end of support for Windows 10, combined with the need for AI-ready hardware, is driving enterprises to refresh their IT systems. Expanding IoT ecosystems are another contributor, with 32% of organizations citing this as a reason for increased data wiping needs. Moreover, the upcoming NIST SP 800-88r2 standards, set to take effect in September 2025, have shifted industry priorities toward more robust media sanitization practices and vendor reliability.
These factors not only emphasize the need for heightened security but also pave the way for more sustainable IT asset management practices.
How ITAD Supports Environmental Goals
Beyond meeting security requirements, certified data wiping aligns with organizations' environmental objectives by promoting sustainable practices.
Certified wiping plays a key role in supporting sustainability efforts by enabling hardware reuse instead of destruction. Unlike physical shredding or degaussing, software-based wiping maintains the physical integrity of devices, allowing them to be refurbished, resold, or donated. This approach maximizes asset recovery while reducing waste.
The scale of the e-waste problem is staggering. Global e-waste reached 61.3 million metric tons in 2023 and is expected to climb to 82 million metric tons by 2030. AI-related hardware alone could contribute as much as 5 million metric tons of e-waste by 2030. By choosing certified wiping over physical destruction, organizations can aim for landfill-free operations without sacrificing security. Notably, 34% of organizations now cite ESG or Net Zero goals as a key motivator for their end-of-life data management strategies.
In regions like the San Francisco Bay Area, companies like Rica Recycling demonstrate how electronics recycling for Bay Area businesses can merge secure data destruction with environmental responsibility. Their commitment to a 100% landfill-free policy showcases how proper data wiping supports responsible electronics recycling while protecting sensitive information. This dual focus helps organizations meet their environmental goals while maintaining robust data security practices.
sbb-itb-855056e
Secure Data Destruction: Exploring NIST 800-88 vs DOD 3-Pass Wipe | ITAMG Insights
New Technologies in Data Wiping
The latest advancements in data wiping technology are tackling modern storage complexities while aligning with environmental objectives. These innovations are designed to handle cutting-edge hardware like NVMe drives and encrypted SSDs, which older methods often struggled to sanitize effectively. Let’s dive into how software, physical methods, and automation are reshaping the way we approach data wiping.
Software-Based Data Erasure
Software-based erasure has become the go-to approach for organizations aiming to securely sanitize data while maximizing the value of their IT assets. The updated NIST SP 800-88 Revision 2, released in September 2025, marks a shift toward enterprise-wide sanitization strategies. This revision also aligns with modern cybersecurity standards like ISO/IEC 27040.
Another key standard, IEEE 2883-2022, addresses gaps in older guidelines by introducing support for modern storage commands across SATA, SCSI, and NVMe devices. Bernard Le Gargean, Product Manager at Blancco, explains:
"IEEE 2883-2022 aims to fill a growing information gap since NIST 800-88 was last revised... it adds support for newer internal commands that improve data sanitization for SATA, SCSI, and NVMe drives".
This standard includes specific commands for clearing NVMe buffers and resetting write pointers, both critical for securely wiping modern storage devices.
Cryptographic Erase (CE) is gaining traction as a preferred method for SSDs and cloud storage. Instead of repeatedly overwriting data, CE deletes encryption keys, making the data unrecoverable in mere seconds. This method avoids the wear-and-tear associated with traditional overwriting, making it particularly effective for flash-based media.
Modern tools are also scaling up efficiency, capable of wiping up to 100 drives per machine or 65,000 drives across a network. These solutions integrate seamlessly with ERP systems like Makor ERP and RazorERP, automating workflows and generating detailed audit trails. New features even detect if devices are enrolled in Apple MDM or Microsoft Autopilot, ensuring compliance with standards like R2 while preparing devices for reuse.
The industry is moving away from outdated practices, leveraging internal firmware commands for faster, more secure erasure. Companies like Workwize emphasize that this approach preserves device functionality, reducing waste and supporting reuse initiatives.
Physical Data Destruction Methods
While software-based erasure is often preferred, physical destruction remains essential for damaged hardware or when the highest levels of security are required.
Shredding involves breaking down storage devices into small particles, with materials like glass, metal, and plastic separated for recycling. Modern shredders are designed for precise cross-cut dimensions to account for the higher data density in today’s storage devices. However, the IEEE 2883-2022 standard raises concerns about shredding’s effectiveness for high-density storage, as it may not guarantee complete data elimination at a microscopic level.
Degaussing, on the other hand, uses strong magnetic fields to erase data on magnetic media. It’s faster and more energy-efficient than shredding, though industrial-grade degaussers can cost over $10,000. However, degaussing only works on magnetic media like traditional hard drives and tapes, leaving SSDs unaffected.
The environmental impact of physical destruction is a growing concern. According to Iron Mountain:
"Disk drive shredding... is also the least environmentally friendly since shredded assets can't be reused or resold and shredded materials can only be recycled".
As a result, organizations are increasingly reserving physical destruction for cases where software-based methods are not feasible, balancing security needs with sustainability goals.
| Method | Security Level | Reusability | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Erasure | High (NIST/IEEE compliant) | Full | Functional drives, sustainability goals |
| Degaussing | High (magnetic media only) | None | Legacy HDDs, tapes |
| Shredding | Highest (physical disintegration) | None | Damaged drives, highest security needs |
Automation and AI in Data Wiping
Automation and AI are revolutionizing data wiping, turning it from a manual and time-consuming process into an industrial-scale operation. With the global ITAD market projected to grow to $54.5 billion by 2030 (up from $25.3 billion in 2025), automation has become a necessity.
AI now acts as a "control tower", analyzing factors like device age, configuration, and security classification to recommend whether assets should be reused, resold, or recycled. Samira Tasneem, an Electronics and Communications Engineer, highlights:
"Automation is the backbone of next-generation ITAD. It is what transforms a fragmented 'services workflow' into an industrial, repeatable, data-rich process".
Automated systems streamline workflows by routing devices to specific stations - whether for wiping, testing, or shredding - based on client policies. AI tools can also identify sensitive data on devices, ensuring the most appropriate sanitization methods are applied. Meanwhile, chain-of-custody monitoring flags anomalies, such as assets scanned onto trucks but not received at processing facilities.
Reporting has also seen a major upgrade. Certificates of Data Destruction are now automatically generated and integrated directly into client ITAM or ERP systems via APIs. This shift from batch-level PDF certificates to item-level API reporting offers real-time visibility and accountability. Some pilot projects are even using blockchain for tamper-proof verification of an asset’s entire lifecycle.
These advancements are speeding up processes, enhancing data security, and enabling more detailed reporting - all while supporting landfill-free operations. Together, these technologies are setting the stage for even more efficient and secure IT asset management.
Data Security and Environmental Responsibility
The IT industry is responsible for about 3% of global CO2 emissions, with global e-waste projected to reach a staggering 82 million metric tons by 2030. Certified data wiping plays a dual role here - it secures sensitive information and extends the life of hardware by enabling reuse instead of sending it to landfills.
In 2024, 34% of organizations adjusted their data management strategies to align with ESG goals and Net Zero commitments. Many are now leaning toward software-based sanitization methods that preserve the value of hardware. As Philip Picciotti from GER puts it:
"The environment and your bottom line also benefit when you achieve greater sustainability and greater value from extending the life of your data storage assets".
This growing focus on sustainability is reshaping data sanitization practices across industries.
E-Waste Recycling and Certified Data Wiping
Certified data wiping offers a way to balance strict security compliance with zero-landfill goals. Using NIST 800-88 "Purge" level sanitization provides the same level of legal protection as physical shredding, but without destroying the hardware. This approach allows functional devices to reenter the circular economy through refurbishment, resale, or donation.
The environmental impact of these practices is substantial. For instance, in 2021, California Electronic Waste Solutions (CEWS) diverted 70 million pounds of e-waste from landfills by combining secure data destruction with refurbishment through R2v3 certified processes. Similarly, the nonprofit Human-I-T has kept 20 million pounds of e-waste out of landfills while providing 523,000 refurbished devices to underserved communities - thanks to NIST 800-88 compliant data sanitization.
For devices that can’t be refurbished, certified recycling processes recover valuable materials like gold, copper, and rare earth metals, while ensuring hazardous components are handled safely. Rica Recycling, for example, operates under a strict zero-landfill policy in the San Francisco Bay Area. They combine secure data destruction certificates with environmentally responsible electronics handling, fully complying with California’s e-waste regulations.
These efforts not only cut down on waste but also prepare devices for extended use, paving the way for practical refurbishment strategies.
Refurbishment and Extending Hardware Life
Software-based data wiping makes hardware reuse both financially and environmentally appealing. Organizations can recover up to 45% of a retired asset's value through resale, while also reducing the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing new devices. With 63% of companies planning to increase IT budgets in 2025, hardware turnover is expected to rise, making refurbishment even more critical.
To protect data while retaining hardware functionality, use NIST "Clear" methods for internal redeployment and "Purge" techniques (such as ATA Secure Erase or Cryptographic Erase) for external resale or donation. As Workwize explains:
"Data erasure, unlike physical destruction, does not render the device useless. This reduces electronic waste and supports circular business models".
Before outsourcing IT asset disposition, remove all BIOS and administrative locks to maximize refurbishment potential. Ensure your ITAD provider holds certifications like R2v3 or e-Stewards, which guarantee high standards for both environmental responsibility and data security. Always request serialized Certificates of Data Destruction to link each wiped device to its serial number, creating a clear audit trail for compliance and sustainability reporting.
Companies are shifting away from "shred-everything" policies in favor of "wipe-and-reuse" strategies. This approach not only supports ESG reporting but also delivers measurable environmental benefits, proving that security and sustainability can go hand in hand.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Strong compliance and thorough reporting are the backbone of certified data wiping. Data destruction isn’t truly complete without documented proof that meets the standards set by HIPAA, GLBA, SOX, and FACTA. Without this documentation, you could face legal risks - even if the data was destroyed properly.
The consequences of non-compliance can be severe. In 2023, Kaiser Foundation Health Plan and Hospitals paid $49 million to settle claims related to improper disposal of protected health information. Penalties for HIPAA violations range from $137 to $68,928 per incident. These aren’t just numbers - they represent significant financial risks tied to inadequate reporting.
As Securis emphasizes:
"A Certificate of Destruction is crucial for proving that an organization has met its legal and regulatory obligations for data security".
To address these needs, ITAD providers utilize digital auditing systems to create tamper-proof records. These systems track every stage of the data destruction process - from collection to final disposal - ensuring a secure and transparent chain of custody.
Certificates of Data Destruction
A Certificate of Data Destruction (CoD) is more than just a piece of paper; it’s your legal proof that data has been permanently erased or destroyed. Compliance with NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 2, the federal guideline for media sanitization, hinges on having this documentation. The latest version of this guideline was updated in September 2025.
A proper certificate doesn’t just check boxes - it provides detailed records. It must include specifics like the device's manufacturer, model, serial number, destruction method (e.g., NIST 800-88 Purge or physical shredding), date and time, and a unique certificate ID. Certificates that only list device counts without serial numbers won’t stand up to scrutiny during an audit.
Professional ITAD providers offer these certificates in 3 to 7 business days, a significant improvement over the industry standard of 30 to 60 days. To maintain a valid audit trail, organizations should retain these certificates for at least two years.
Digital Auditing and Verification Systems
Cloud-based digital auditing systems take compliance to the next level by creating permanent, tamper-proof records. These systems generate erasure reports that, once created, cannot be altered - offering a higher level of trust during audits.
These platforms often integrate directly with ERP systems like Makor ERP and RazorERP, automatically syncing destruction data with asset management records. This eliminates manual data entry errors and ensures a seamless audit trail from the moment a device is retired to its final disposal. With 24/7 access, organizations can easily respond to auditor requests or compliance reviews.
Verification tools like HexViewers allow technicians to confirm that data has been fully overwritten. Automated checks can also detect whether devices are enrolled in MDM (Mobile Device Management) or Autopilot, ensuring they’re cleared for reuse. Some systems even have the capability to wipe up to 65,000 drives simultaneously over a network, producing individual reports for each device.
BitRaser highlights the compliance benefits of these systems:
"BitRaser's erasure reports help you to meet audit requirements & comply with global data privacy laws, regulations & standards like – EU GDPR, GLBA, SOX, HIPAA, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, etc."
When choosing an ITAD provider, it’s essential to confirm they hold certifications like NAID AAA, R2v3, or e-Stewards. These certifications require regular, unannounced audits to ensure the integrity of destruction and reporting processes. For example, Rica Recycling, based in the San Francisco Bay Area, offers serialized Certificates of Data Destruction as part of their R2v3-certified services. This ensures compliance with both California’s e-waste regulations and federal data security standards. Such digital records provide seamless support for decisions on whether to handle data destruction on-site or off-site.
On-Site vs. Off-Site Data Destruction
Deciding whether to destroy your data at your own facility or at a vendor's location depends on the sensitivity of the information and how much risk you're comfortable taking. On-site destruction keeps everything within your control until the data is destroyed, while off-site destruction uses large-scale facilities to handle bigger volumes more efficiently. Both options can align with standards like NIST SP 800-88, but they cater to different security and operational priorities.
On-Site Data Destruction
On-site data destruction involves bringing mobile shredders or crushers directly to your location. This ensures that sensitive data never leaves your premises in a readable format, eliminating any risks tied to transporting devices. Your team can oversee the process, giving you immediate visual confirmation that hard drives, SSDs, or tapes have been physically destroyed.
This method is particularly suited for organizations that deal with highly sensitive or regulated information - think federal defense contractors, financial institutions, forensic labs, or healthcare providers managing Protected Health Information (PHI). While on-site destruction tends to be more expensive and resource-intensive, the added security often justifies the cost for small batches or urgent decommissioning projects.
Off-Site Data Destruction
Off-site destruction involves collecting, cataloging, and transporting your retired devices to a secure facility equipped with industrial shredders and degaussers. This approach allows for efficient processing of large volumes using advanced machinery.
Security during transit is a key factor. Trusted ITAD providers use GPS-tracked vehicles, locked trucks, and tamper-evident seals to ensure a secure chain of custody from pickup to destruction. Once at the facility, devices are logged, processed, and tracked using digital systems that provide serialized Certificates of Data Destruction.
Off-site destruction is a practical choice for organizations with standard security needs, especially those handling large-scale hardware refreshes or managing distributed assets. It strikes a balance between security and cost-efficiency for routine corporate hardware. However, you’ll want to confirm that your vendor holds certifications like NAID AAA, R2v3, or e-Stewards to ensure compliance with industry best practices.
How to Choose the Right Method
When deciding between these methods, consider the sensitivity and volume of your data. For assets containing PHI, personally identifiable information (PII), intellectual property, or classified government data, on-site destruction offers the highest level of control and reduces risk by keeping the process entirely under your supervision. On the other hand, off-site destruction is often more cost-effective and efficient for standard corporate hardware, provided the vendor maintains strict chain-of-custody protocols.
On-site destruction typically comes with higher per-device costs, making it ideal for smaller, time-sensitive projects. Meanwhile, off-site methods are better suited for handling large batches. Some organizations combine strategies, performing on-site cryptographic erasure or degaussing before sending devices for off-site physical destruction. Regardless of the method, always ensure your ITAD provider issues a serialized Certificate of Data Destruction for every device.
For businesses in California, Rica Recycling offers both on-site and off-site data destruction services. With full R2v3 certification, they ensure compliance with state e-waste regulations and federal data security standards.
Conclusion: What's Next for Data Wiping in ITAD
The future of data wiping in IT asset disposition (ITAD) is leaning heavily toward software-based erasure methods that preserve the value of hardware. With the upcoming release of NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 2 in September 2025 and the growing adoption of IEEE 2883 standards, organizations now have clearer guidelines for securely sanitizing modern storage devices like NVMe drives and SSDs. These standards prioritize "Purge" and "Clear" methods, which not only ensure data security but also allow devices to remain functional for resale or donation - directly aligning with circular economy goals. These updates build on the robust frameworks already in place.
At the same time, regulatory and compliance demands are becoming more stringent. Enterprises are responding by ramping up their investments in data privacy and protection, with 58% increasing spending by an average of 46% during 2024-2025. Digital auditing systems have become essential, offering serialized Certificates of Data Destruction for each asset. These certificates create tamper-proof verification trails, which are crucial for meeting regulatory requirements. With hardware refresh cycles accelerating - spurred by Windows 10's end of support and the rise of AI-driven tools - the number of devices requiring certified data wiping is only set to increase.
Beyond regulatory compliance, there’s a growing push to reduce Scope 3 emissions, encouraging organizations to adopt landfill-free ITAD solutions. Many are shifting away from disposal-focused practices in favor of refurbishment and remarketing services, which not only extend the life of technology but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions and e-waste. These efforts are becoming a critical element of ESG reporting frameworks.
"ITAD is increasingly focused on the environmental sustainability benefits of extending the lifecycle of technology assets to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and e-waste." – Gartner
For businesses navigating these changes, Rica Recycling offers a comprehensive solution. Their R2v3-certified services and 100% landfill-free policy align with California's stringent e-waste regulations. Operating in the San Francisco Bay Area, they provide both on-site and off-site destruction options. Partnering with certified local providers like Rica Recycling ensures that organizations can meet evolving security, compliance, and sustainability requirements effectively.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using software-based data wiping instead of physical destruction?
Software-based data wiping comes with several standout advantages over physical destruction. For one, it’s both budget-friendly and better for the environment. By skipping the need to physically destroy devices, it minimizes electronic waste and aligns with efforts to reduce environmental impact. Plus, it gives IT hardware a second life - whether through reuse or resale - helping businesses make the most of their investments.
Another big perk is the ability to obtain certifications for compliance, guaranteeing that data has been erased securely and meets industry regulations. This method is also incredibly adaptable, working seamlessly across various device types. For businesses handling IT asset disposition (ITAD), it offers a practical and efficient way to manage data removal.
What impact does NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 2 have on data wiping practices?
The latest update to NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 2 sets tougher standards for data wiping, aiming to improve security and compliance in IT asset disposition (ITAD). Key changes include a focus on formal sanitization validation, refreshed guidance for handling modern storage devices, and the integration of recommendations from the IEEE 2883:2022 standard. These updates strengthen the effectiveness and reliability of data erasure practices.
Another noteworthy update is the revision of the certificate of erasure, simplifying the process of verifying and documenting compliance. By adhering to these standards, organizations can safeguard sensitive data more effectively and stay aligned with evolving regulatory expectations.
How does certified data wiping support sustainability and ESG initiatives?
Certified data wiping plays a crucial role in securely erasing sensitive information from IT devices, making them suitable for reuse or responsible recycling. This process helps keep electronic waste out of landfills, reducing the environmental footprint associated with IT asset disposal.
On top of that, certified data wiping gives organizations the documentation they need to meet Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals and comply with standards like R2v3, ADISA, and e-Stewards. By ensuring data security and encouraging device reuse, businesses can stay true to their sustainability commitments while supporting a circular economy.
