Data Security Tips for Nonprofits Recycling Electronics
Recycling electronics without securely erasing data can expose nonprofits to serious risks. Sensitive donor records, financial details, and other private data can be recovered even after files are "deleted." A single breach could cost nearly $5 million and destroy donor trust. Here's how to protect your nonprofit:
- Document all devices: Include laptops, phones, printers, and more. Create an inventory noting make, model, and serial numbers.
- Wipe data securely: Follow NIST 800-88 guidelines. Use certified software to erase data or physically destroy media for sensitive devices.
- Encrypt devices: Enable full-disk encryption and remove SIM/SD cards before recycling.
- Choose certified recyclers: Look for R2v3 or e-Stewards certifications. Request a Certificate of Data Destruction for legal protection.
Avoid shortcuts. Deleting files or factory resets won’t fully erase data. Secure destruction and certified recyclers reduce risks and ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
Secure Disposal/Shredding of Information
sbb-itb-855056e
How to Ensure Secure Data Destruction
Before recycling your electronics, it’s crucial to have a solid plan for protecting your data. Simply deleting files or formatting a hard drive won’t cut it - those files can often be recovered with the right software. Here’s how to make sure your sensitive information stays safe.
Create an Inventory of All Electronics
Start by documenting every device that might hold sensitive data. For each one, note the make, model, serial number, and year of purchase. Don’t just think about computers - include smartphones, tablets, external hard drives, digital cameras, and even office equipment like printers and copiers, as these can store document images and network credentials.
Search everywhere: storage rooms, server areas, and even equipment used by remote employees. Samira Tasneem from GreenCitizen offers this advice:
"Tag each computer with a unique identifier (barcode, asset tag, or RFID) before recycling. This not only streamlines chain-of-custody tracking but also makes compliance reporting and ESG audits far easier".
Once you’ve got your list, sort the devices into three groups: ones that still work and could be donated or resold, broken items that need recycling, and sensitive devices like executive laptops or HR servers that require certified destruction.
Wipe Data Using NIST 800-88 Standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has clear guidelines for securely erasing data, updated in September 2025. Their NIST 800-88 framework outlines three levels of data sanitization: Clear, Purge, and Destroy. For most situations, purge-level sanitization is enough to protect sensitive data while keeping the device usable.
Certified software tools can wipe data from working devices, but don’t forget about less obvious items like printers, copiers, and VoIP phones, which also store data. Additionally, keeping encryption enabled on your devices during this process adds an extra layer of security.
Encrypt Devices Until Drop-Off
Full-disk encryption is a must for protecting your data during transport. For mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, Mobile Device Management (MDM) tools come in handy - they allow you to remotely lock or wipe devices if something goes wrong during transit.
Before handing over your electronics, remove SIM and SD cards. And, of course, back up any important files to a secure cloud service or external drive before starting the data sanitization process to avoid accidental loss.
Choosing a Certified Electronics Recycler
Once your devices are prepped, the next step is finding a recycler that prioritizes data security and follows legal requirements for handling electronics. The certifications a recycler holds can tell you a lot about their commitment to protecting your data and managing waste responsibly.
Look for R2v3 and e-Stewards Certifications

Two certifications you should pay attention to are R2v3 (Responsible Recycling) and e-Stewards. Both are widely recognized by the EPA and are considered top-tier standards, though they emphasize slightly different aspects of recycling.
R2v3, managed by SERI, focuses on strong security measures, effective data sanitization, and accountability throughout the recycling process. In 2020, the standard was updated to include stricter rules for tracking hazardous materials and ensuring downstream vendors meet quality standards. Achieving R2 certification is no small feat - it usually takes a company 8 to 12 months to meet the international requirements.
e-Stewards, developed by the Basel Action Network (BAN), takes a more ethical stance by banning the export of hazardous e-waste to developing nations. This certification also collaborates with NAID AAA to perform detailed audits of data destruction practices, ensuring top-notch data security. According to e-Stewards:
"e-Stewards Certified electronics recyclers and refurbishers are the trusted destination for all of your retired electronic assets".
To confirm a recycler’s certification, use the official directories on the SERI or e-Stewards websites. Don’t rely solely on their claims - verify it yourself. Once confirmed, ask for documented proof of data destruction to ensure your security measures are complete.
Request a Certificate of Data Destruction
After choosing a certified recycler, make sure to get a Certificate of Data Destruction. This document serves as legal proof that your data has been permanently erased, protecting your organization under regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and FACTA. For instance, healthcare facilities risk fines of up to $50,000 per incident if sensitive patient data is left on recycled devices.
The certificate should include details such as the serial numbers of the devices, the destruction date, the method used (aligned with NIST 800-88 standards), and the issuer’s information. Typically, recyclers provide this certificate within one to six weeks.
Opt for recyclers with NAID AAA certification, which ensures their data destruction processes undergo rigorous third-party audits to meet stringent security standards. Liz Cooper from Human-I-T highlights its importance:
"NAID AAA Certification is the gold standard for data destruction. Organizations with this certification undergo rigorous third-party audits to verify their processes meet strict security protocols".
Finally, maintain a documented chain of custody from your facility to the point of destruction. This is your strongest defense in case of an audit. A 2020 investigation revealed that nearly 20% of used hard drives sold on the open market still contained personally identifiable information (PII) - a stark reminder of why thorough documentation and secure processes are crucial.
Best Practices for Free E-Waste Drop-Off Events
Free e-waste drop-off events are a great way for nonprofits to recycle old electronics responsibly. However, not all events follow the same data security standards. Before handing over your devices, it’s important to dig into the details of how they’ll be handled after drop-off.
Verify Event Providers' Security Measures
Start by checking if the event organizers work with recyclers who hold NAID AAA Certification or R2 (Responsible Recycling) credentials. These certifications ensure that the recycler has undergone strict third-party audits for secure data destruction. Don’t hesitate to ask for the name of the recycling partner and verify their certification through official directories.
You’ll also want to learn about their chain of custody procedures. Reputable providers use measures like GPS-tracked vehicles, tamper-evident containers, and secure staging areas to monitor devices from collection to destruction. Additionally, make sure their personnel have passed criminal background checks and signed confidentiality agreements. Facilities should have video surveillance in place, with at least 90 days of footage stored.
Finally, ask for a Certificate of Data Destruction. While some providers may charge for this document, it’s critical to have legal proof that your data was securely erased.
Once you’ve confirmed the recycler’s security practices, it’s time to prepare your devices for safe transit.
Prepare Devices for Drop-Off
Even when working with certified recyclers, taking a few extra steps to prepare your devices can help protect sensitive information. Begin by signing out of all cloud accounts, such as iCloud or Google. This prevents devices from being activation locked, which can make them unusable even after a factory reset. Double-check all ports and slots for SIM cards, SD cards, or USB drives that might still hold personal data.
Remove any asset tags, labels, or stickers that identify your nonprofit. These physical identifiers could pose a risk if the devices are mishandled. For devices that once stored highly sensitive information, consider enabling full disk encryption after wiping the data to further obscure any remaining traces. Lastly, create a detailed inventory of all devices you plan to drop off to maintain accountability.
Rica Recycling's Data Security and Sustainability Services
Bay Area nonprofits can make recycling easier and safer by working with a certified local provider like Rica Recycling. They specialize in secure data destruction and responsible e-waste handling, tailored for organizations that need dependable documentation and compliance support. These services tie into strong data management practices, ensuring nonprofits can manage their sensitive information with confidence.
Certified Data Destruction for Nonprofits
Rica Recycling employs certified software to erase data in line with NIST 800-88 and DoD 5220.22-M standards. For hard drives, they go further with industrial degaussing or, for highly sensitive data, physical shredding to guarantee complete data removal.
Once your devices are processed, they provide a Certificate of Data Destruction. This document serves as legal proof that your nonprofit’s data was securely erased, which is critical for audits and maintaining donor trust. Their process also fully complies with California’s e-waste regulations, ensuring every device is handled responsibly under a strict 100% landfill-free policy. Partnering with Rica Recycling means nonprofits can meet compliance standards while safeguarding sensitive information.
E-Waste Drop-Off and Pickup Options
Beyond secure data destruction, Rica Recycling makes recycling logistics simple. They offer flexible solutions tailored to the number of devices you need to recycle.
- For up to 9 items: Nonprofits can drop off computers, phones, and similar devices for free. Appliance recycling, however, incurs a $50 fee per item at drop-off.
- For 10 or more items: Pickup services are available throughout the Bay Area, with costs ranging from $50 to $200 based on the type of equipment. Pickup service includes certified data destruction, while drop-off requires you to erase data beforehand.
Both options ensure your e-waste stays out of landfills, supporting California’s commitment to managing over 200,000 tons of e-waste generated annually.
Data Destruction Methods Compared
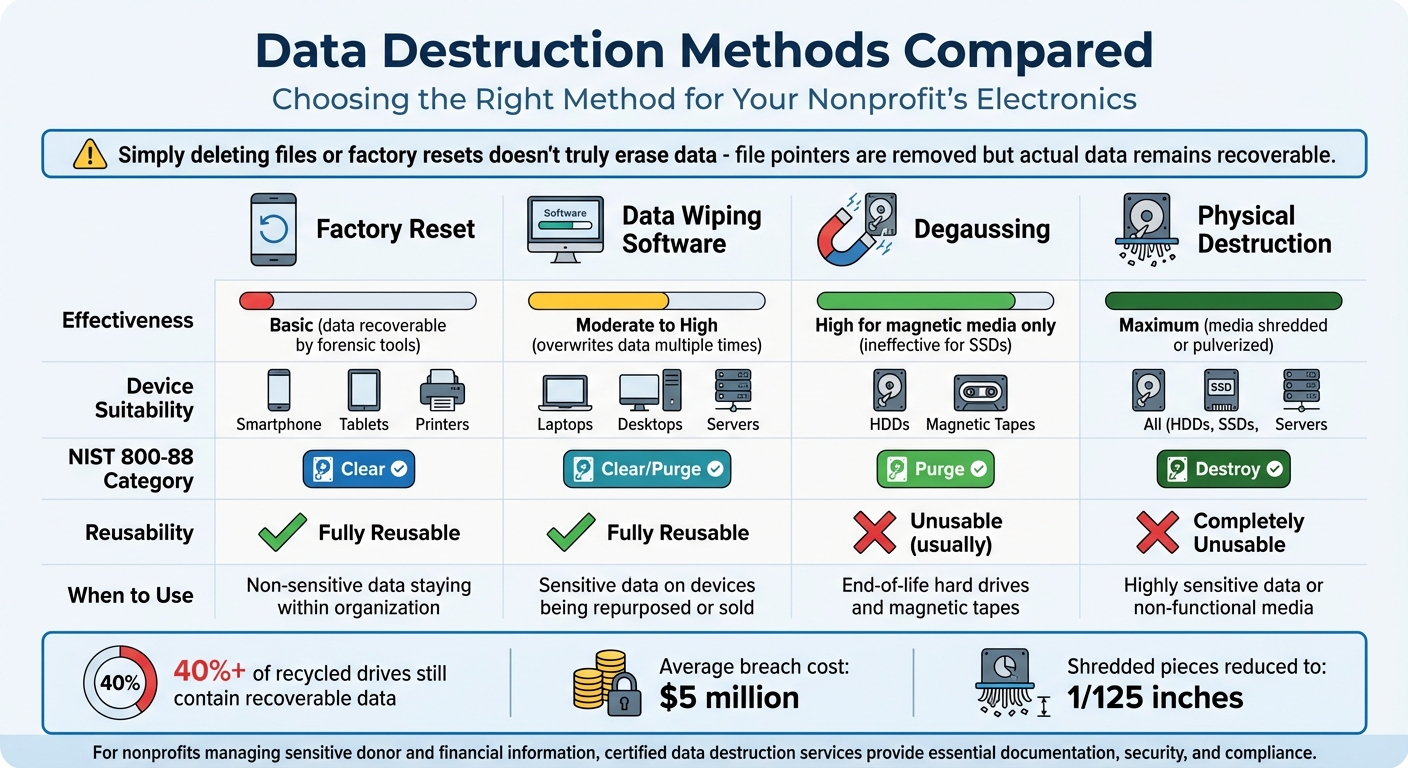
Data Destruction Methods Comparison for Nonprofits: Effectiveness, Suitability, and When to Use
Choosing the right data destruction method is critical to avoid costly mistakes. For example, Morgan Stanley Wealth Management faced a $35 million settlement with the SEC in September 2022 after hiring a moving and storage company with no expertise in data destruction. This misstep exposed the personal identifying information (PII) of approximately 15 million customers from thousands of improperly decommissioned hard drives and servers.
Using secure data destruction practices, as outlined by the NIST 800-88 guidelines (updated to Revision 2 as of September 26, 2025), ensures data is handled properly. These guidelines categorize destruction methods into three levels: Clear, Purge, and Destroy.
- Clear: Relies on basic software overwrites to protect against standard recovery tools but may fail to address hidden sectors.
- Purge: Uses advanced techniques like cryptographic erasure to defend against forensic recovery.
- Destroy: Physically destroys media, such as shredding or pulverizing, leaving no chance for data recovery. Shredded pieces are reduced to no larger than 1/125 inches to prevent reconstruction.
Why Degaussing Has Limits
Degaussing, which uses powerful magnetic fields to disrupt magnetic media, is increasingly outdated. While effective for traditional hard drives and magnetic tapes, it’s useless for flash memory devices like SSDs, smartphones, and tablets. According to NIST, "Degaussing, a fundamental way to sanitize magnetic media, no longer applies in most cases for flash memory-based devices". Even for magnetic drives, household magnets won’t cut it - modern hard drives are designed to resist magnetic interference, and data often remains recoverable.
Comparison Table: Data Destruction Methods
| Method | Effectiveness | Device Suitability | NIST 800-88 Category | Reusability | When to Use Certified Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factory Reset | Basic; data recoverable by forensic tools | Smartphones, Tablets, Printers | Clear | Fully Reusable | For non-sensitive data staying within the organization |
| Data Wiping Software | Moderate to High; overwrites data multiple times | Laptops, Desktops, Servers | Clear / Purge | Fully Reusable | For sensitive data on devices being repurposed or sold |
| Degaussing | High (magnetic media only); ineffective for SSDs | HDDs, Magnetic Tapes | Purge | Unusable (usually) | For end-of-life hard drives and magnetic tapes |
| Physical Destruction | Maximum; media shredded or pulverized | All (HDDs, SSDs, Servers) | Destroy | Completely Unusable | For highly sensitive data or non-functional media |
Why Deletion Isn’t Enough
Simply deleting files or performing a factory reset doesn’t truly erase data. These actions only remove file pointers, leaving the actual data intact and recoverable with basic tools. For nonprofits managing sensitive donor and financial information, certified data destruction services are essential. They provide the documentation, security, and compliance needed to protect trust and meet legal requirements effectively.
Conclusion
Nonprofits handle sensitive records, including donor information, financial data, and employee files. Improper disposal of electronics can jeopardize all of this. A 2024 study revealed that over 40% of recycled drives still contained recoverable data. With breaches averaging nearly $5 million per incident, there’s no room for mistakes. The stakes couldn’t be higher.
The solution is clear: keep a detailed inventory, use NIST 800-88 compliant data wiping methods, and work with certified recyclers. As Human-I-T emphasizes:
"When done properly, donation becomes the safest disposal method for you and the most impactful choice for your community".
Instead of shredding, securely wiping functional devices allows nonprofits to refurbish electronics for schools and underserved communities. This approach not only ensures data security but also creates meaningful social impact. Partnering with recyclers certified under R2v3 or e-Stewards guarantees your electronics are processed with strict environmental and security protocols.
For nonprofits in the Bay Area, finding the right partner is essential. Rica Recycling offers tailored services, including flexible pickup and drop-off options for community collection events. Their 100% landfill-free processing ensures every device undergoes proper data destruction, with Certificates of Destruction provided as legal proof for audits.
Compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA is non-negotiable, as violations can lead to severe penalties. By working with certified providers, nonprofits can safeguard donor trust, meet compliance standards, and contribute to environmental responsibility - all in one step.
Avoid relying solely on recycling centers for data destruction. Industry experts caution:
"Recycling centers wipe everything for you. Some do, but never assume - always wipe first".
Take charge of your data security. Verify certifications, document every step, and ensure each device is handled properly from collection to destruction.
FAQs
Why is it important to securely erase data before recycling electronics?
Failing to properly erase data before recycling electronics can leave sensitive information - like personal details, financial records, or confidential business data - vulnerable. This opens the door to identity theft, data breaches, and unauthorized access to private information.
The consequences can be severe: financial losses, legal troubles, reputational damage, and even the exposure of proprietary information. To safeguard yourself and your nonprofit, make sure all devices go through thorough and secure data destruction before recycling. It’s a simple step that can prevent a lot of headaches down the line.
How can nonprofits ensure their electronics recycler is certified?
To make sure an electronics recycler is certified, nonprofits should look for recognized certifications such as R2 or e-Stewards. These certifications confirm that the recycler adheres to strict standards for protecting the environment, securing data, and managing e-waste responsibly.
To verify a recycler's certification, check official directories from organizations like SERI or e-Stewards. This helps ensure your nonprofit works with a trusted partner, keeps sensitive data safe, and promotes responsible recycling practices.
Why is physically destroying data sometimes the best option?
Physically destroying data is often the most surefire way to make sure sensitive information is gone for good. Even if you delete files or wipe a device, advanced recovery methods can sometimes bring that data back, creating a potential risk for data breaches.
By physically destroying hard drives or other storage devices, you completely remove the possibility of anyone accessing the data. This approach is especially crucial for nonprofits managing confidential donor details, financial records, or other sensitive information that needs to stay protected.
