How ITAD Providers Ensure Data Center Compliance
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) is essential for securely retiring outdated IT equipment while meeting legal and environmental requirements. Without proper ITAD processes, organizations risk data breaches, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. For example, Morgan Stanley faced a $60 million fine after failing to use a certified ITAD provider, leading to exposed customer data.
Here’s how certified ITAD providers protect organizations:
- Data Security: They follow standards like NIST 800-88 Rev. 2, ensuring data is irrecoverable through methods like overwriting, degaussing, or physical destruction.
- Regulatory Compliance: Certifications such as NAID AAA and R2v3 provide verified proof of compliance with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and California e-waste regulations.
- E-Waste Management: Providers adhere to policies like ISO 14001 and e-Stewards, ensuring safe recycling practices and avoiding landfill contributions.
- Audit-Ready Documentation: Certificates of Destruction and chain-of-custody records protect organizations during regulatory reviews.
Using a certified ITAD provider minimizes risks, ensures compliance, and promotes responsible disposal practices for data center equipment.
The Enterprise ITAD Playbook (2025): Secure, Compliant IT Asset Disposition at Scale
sbb-itb-855056e
Compliance Regulations for Data Center Asset Recovery
When it comes to data center asset recovery, understanding the relevant regulations is crucial. These rules are designed to safeguard sensitive data and ensure responsible handling of e-waste. Missteps can lead to data breaches, hefty fines, or reputational harm. Below, we’ll explore the major frameworks that guide compliance in IT asset disposition (ITAD).
Major Regulations and Frameworks
NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 2 is the go-to U.S. government standard for media sanitization. Finalized in September 2025, it outlines three methods for data destruction: Clear (software-based overwriting), Purge (cryptographic erasure or degaussing), and Destroy (physical methods like shredding). While this standard offers detailed technical guidance, it’s important to note that it’s not a certification but a self-applied framework organizations adhere to.
R2v3 (Responsible Recycling) is an internationally recognized certification that emphasizes both environmental responsibility and data security. It requires vendors to conduct downstream due diligence and implement strict sanitization processes. Adherence is validated through third-party audits conducted by SERI-accredited bodies.
NAID AAA Certification, issued by i-SIGMA, is widely regarded as the gold standard for verified data destruction. This certification mandates unannounced audits, employee background checks, and a secure chain of custody. It’s particularly relevant for compliance with laws like HIPAA and GLBA. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in legal and financial consequences, as well as damage to your organization’s reputation.
ISO 14001:2015 is a global standard that focuses on environmental management. It ensures proper handling of e-waste and hazardous materials in line with environmental laws. Similarly, e-Stewards certification enforces ethical e-waste practices, including a strict prohibition on exporting hazardous waste to developing nations, backed by rigorous third-party audits.
In addition to these frameworks, industry-specific regulations like HIPAA, GLBA, and SOX require documented destruction of sensitive data. Government contractors must also comply with NISPOM 32 CFR Part 117 and NSA/CSS Policy Manual 9-12 for the disposal of classified or controlled unclassified information (CUI).
California imposes additional e-waste laws, requiring the recycling of hazardous electronic components such as lead-acid batteries and mercury-containing devices. For organizations in areas like the San Francisco Bay Area, adherence to these state-level regulations is mandatory.
Compliance Standards Comparison
Here’s a quick look at how the key standards and certifications stack up:
| Standard/Certification | Primary Focus | Key Requirements | Certification Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIST 800-88 Rev. 2 | Data Security | Defines Clear, Purge, and Destroy methods for media sanitization. | Self-applied standard (not a certification). |
| R2v3 | Environmental & Security | Downstream due diligence, testing/repair for reuse, and data destruction. | Audited by SERI-accredited bodies. |
| NAID AAA | Data Security | Unannounced audits, employee screening, and secure chain of custody. | Audited by i-SIGMA. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental | Management of hazardous materials and e-waste recycling practices. | Third-party management system audit. |
| e-Stewards | Environmental | Ethical global e-waste practices and prohibition of hazardous waste export. | Audited by Basel Action Network (BAN). |
Why Certifications Matter
It’s important to distinguish between standards and certifications. While many vendors may claim to "follow" NIST 800-88, only certifications like NAID AAA or R2v3 provide verified, audit-ready proof of compliance. If your vendor fails to comply, the liability often falls on your organization. Without proper documentation, you could face regulatory penalties, even if the mistake wasn’t yours.
The ITAD Compliance Process for Data Centers
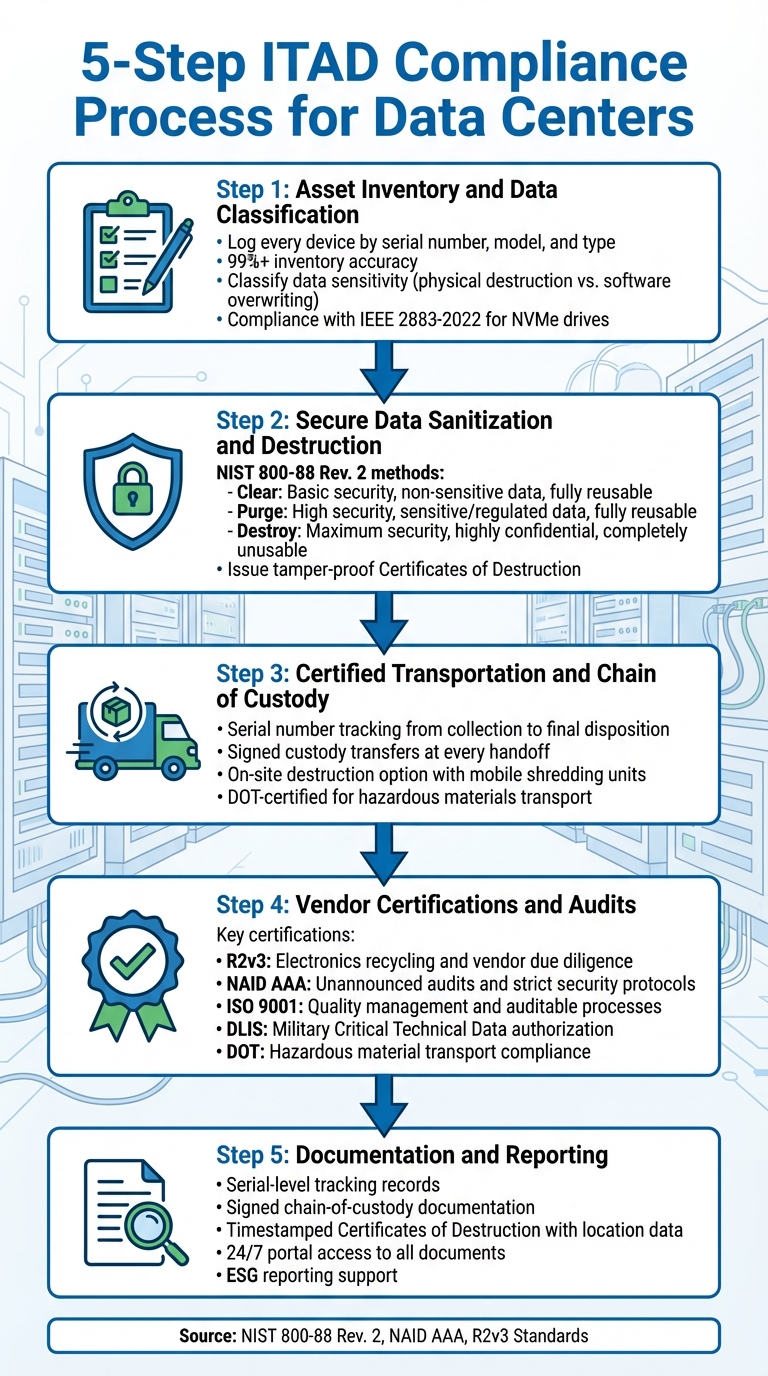
5-Step ITAD Compliance Process for Data Centers
Professional ITAD providers follow a detailed process to ensure data center asset recovery adheres to all regulations. This approach safeguards sensitive data, meets legal requirements, and aligns with environmental standards.
Step 1: Asset Inventory and Data Classification
The process starts with creating a detailed inventory of every device in your data center. ITAD providers log each asset by serial number, model, and type, covering everything from servers and storage arrays to networking equipment and backup drives. Inventory systems are highly accurate, achieving 99%+ precision.
At the same time, data classification is performed. Devices are assessed for sensitive information, determining whether they require physical destruction or software-based overwriting. For example, equipment with classified data is destroyed, while non-sensitive devices may be refurbished and resold. This step also ensures compliance with updated standards like IEEE 2883-2022, which is critical for modern NVMe drives.
Step 2: Secure Data Sanitization and Destruction
Once assets are inventoried and classified, the next step is data destruction. Providers use methods outlined in NIST 800-88 Rev. 2 - Clear, Purge, or Destroy - depending on data sensitivity and reuse potential.
- Clear: Suitable for non-sensitive data; uses standard IT tools.
- Purge: Targets sensitive or regulated data; requires advanced expertise.
- Destroy: Designed for highly confidential data; renders devices completely unusable.
Here’s a quick comparison of these methods:
| Factor | Clear | Purge | Destroy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Level | Basic (standard tools) | High (advanced forensics) | Maximum (irrecoverable) |
| Data Sensitivity | Non-sensitive | Sensitive or regulated | Highly confidential |
| Device Reusability | Fully reusable | Fully reusable | Completely unusable |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal | Minimal | Higher (due to destruction) |
After destruction, providers issue Certificates of Destruction, which are tamper-proof and ensure compliance. These certificates confirm that data has been securely sanitized.
Step 3: Certified Transportation and Chain of Custody
Transporting data center equipment to a processing facility introduces risks, making a secure chain of custody essential. ITAD providers track each device by serial number from collection to final disposition .
"Without chain-of-custody documentation, your organization may be unable to prove compliance, even if the data was destroyed." - Securis
Providers use signed custody transfers at every handoff point, creating a clear record of responsibility. For high-security environments, on-site destruction eliminates transit risks entirely. Mobile shredding units can destroy assets at your facility before they leave the premises.
Additionally, transporting devices with hazardous materials like lithium-ion batteries, lead, or mercury requires a DOT-certified provider to ensure legal and safe handling.
Step 4: Vendor Certifications and Audits
Certified vendors undergo regular audits to meet compliance standards. Key certifications include:
| Certification | Focus Area | Key Compliance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| R2v3 | Electronics Recycling | Ensures vendor due diligence and safe recycling |
| NAID AAA | Data Destruction | Unannounced audits and strict security protocols |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management | Guarantees repeatable, auditable processes |
| DLIS | Military Data | Authorized for handling Military Critical Technical Data |
| DOT | Transportation | Complies with hazardous material transport laws |
The NAID AAA certification is especially critical as it includes unannounced audits, employee background checks, and strict custody protocols . These certifications ensure your ITAD provider follows verified best practices.
Step 5: Documentation and Reporting
"When an audit hits, it's not enough to say your data was destroyed - you need proof." - Securis
Comprehensive documentation protects your organization from liability. ITAD providers supply detailed reports that include serial-level tracking, signed chain-of-custody records, and certificates of destruction with timestamps and location data .
Top providers also offer 24/7 portal access to these documents , keeping you prepared for audits or Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) requests. Additionally, this documentation supports ESG reporting, demonstrating your commitment to responsible recycling practices.
How Rica Recycling Ensures ITAD Compliance
Rica Recycling provides certified ITAD services tailored to businesses, schools, and government agencies across the San Francisco Bay Area. Their expertise lies in data center asset recovery, covering everything from server removal and rack decommissioning to cable harvesting and secure transport. These services are designed to uphold regulatory standards and protect sensitive data, aligning with frameworks such as NIST and NAID AAA.
Certified Electronics Recycling and Data Destruction
To meet ITAD compliance requirements, Rica Recycling collaborates with R2v3 and EPA-registered processors. This ensures IT assets are handled according to stringent industry protocols. Clients receive serialized Certificates of Destruction that detail each device's make, model, serial number, and destruction status. These certificates provide the necessary documentation for audits and help meet regulatory demands.
Environmentally Responsible Practices
Rica Recycling follows a strict 100% landfill-free policy. Every component is either refurbished for reuse or recycled responsibly. The company complies with California SB20 and SB50 regulations, which enforce state-approved recycling standards for electronic waste. With over 7 million tons of e-waste generated annually in the U.S. and only 15–20% properly recycled, Rica Recycling addresses this growing issue head-on. For perspective, recycling just 273 laptops saves enough energy to power an average U.S. home for a year.
Convenient Pickup and Drop-Off Options
Rica Recycling offers flexible options for IT asset disposal, including scheduled on-site pickups and coordinated logistics throughout the San Francisco Bay Area. For data centers, pickup schedules are designed to align with decommissioning timelines while maintaining strict security measures. Additionally, their IT asset buyback programs allow organizations to recover value from remarketable equipment. Pricing depends on factors like volume, labor, and data destruction requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting a certified ITAD provider is a smart way to avoid the financial and legal pitfalls tied to improper data center asset disposal. The risks of non-compliance - like data breaches and hefty regulatory fines - make certified processes and audit-ready documentation essential. Without proper records, your organization could still face liability if a vendor fails to meet required standards.
Certified providers take on the technical challenges, adhering to NIST 800-88 standards while ensuring a secure chain of custody through GPS-tracked transport and serialized asset logging. This documentation isn’t just a formality - it’s a critical safeguard during regulatory reviews or legal investigations. Considering that 68% of data breaches stem from weaknesses in outdated or idle systems, secure data sanitization plays a key role in managing risk.
The environmental aspect is just as important. As mentioned earlier, global e-waste continues to climb while recycling rates struggle to keep up. Certified ITAD providers committed to 100% landfill-free policies ensure your retired equipment avoids contributing to this issue, aligning with your organization's ESG goals.
"Compliance is a shared responsibility. Even with a certified ITAD provider, your organization remains accountable. If your organization can't produce audit-ready documentation, liability falls on you, even if the vendor failed." - Securis
FAQs
What certifications ensure ITAD providers meet compliance standards?
To stay compliant, ITAD providers should maintain important certifications such as R2 or R2v3, NAID, e-Stewards, and RIOS. These credentials confirm that the provider follows strict protocols for secure data destruction, responsible recycling, and ethical practices.
Working with a certified provider ensures sensitive data is safeguarded, regulatory standards are met, and efforts toward sustainability are upheld during IT asset recovery.
How do certified ITAD providers help protect businesses from data breaches?
Certified ITAD providers are essential in protecting sensitive data by employing secure and compliant methods for data destruction. They adhere to established industry standards like NIST 800-88 to guarantee that all data is completely erased or destroyed, leaving no chance for recovery.
Moreover, these providers maintain detailed audit trails, giving businesses the documentation they need to confirm that their assets were managed securely and responsibly. This approach not only minimizes the risk of data breaches but also helps companies stay compliant with regulations and steer clear of potential legal or financial consequences.
Why is maintaining a secure chain of custody critical in ITAD processes?
Maintaining a secure chain of custody is critical in IT asset disposition (ITAD) because it ensures accountability at every step - whether handling, transporting, or disposing of IT assets. This documented process is designed to safeguard sensitive data, prevent theft, and meet regulatory compliance standards.
By meticulously tracking devices from start to finish, companies can minimize the risk of data breaches, show compliance with legal obligations, and uphold trust with their stakeholders. A secure chain of custody is a key part of managing IT assets responsibly.
